Storing Crypto Private Keys in Environment Variables is Dangerous: Use a TEE
Environment variables do not offer strong enough protection for high-value crypto private keys. Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) like AWS Nitro Enclaves provide cryptographic isolation that closes common attack vectors.
On December 3, 2025, the React Team informed the web development community of CVE-2025-55182. It received a CVSS rating of 10.0. It literally doesn’t get any worse.
This rating was given for good reason; it allows pre-authentication remote code execution. This means an attacker can (among other things) obtain any values located in files on the host machine or environment variables. Did you “safely" load your crypto private key into memory from environment variables in your server-side JavaScript process? In one instance of misplaced trust, your funds, and your company’s reputation are lost.
As one developer put it, "My guess is this won’t be the last time we see security fallout from that design choice. Not because React is sloppy, but because it’s trying to solve a problem category that traditionally requires explicitness, not magic.”
Private keys are fundamentally different than other sensitive values like database connections and API Keys. Leaked private keys cannot be rotated or revoked. You have one chance to secure your private key.
Loading crypto private keys into your application runtime using environment variables leaves you vulnerable to exploits from dependencies (like CVE-2025-55182), operating system-level vulnerabilities, and issues from underlying infrastructure providers. Is this the kind of risk you want to take?
There’s a better architectural approach: a cryptographically-isolated key management service that still allows you to use convenient tools (like React Server Components) for application logic, while preserving the security of your private keys.
Understanding Trusted Execution Environments
The React Server Components CVE proves that keys in your application memory or file system are exposed. Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) are secure and isolated places to perform sensitive operations.
Your application sends signing requests to a TEE, but can never extract the key itself. Even if an attacker fully compromises your dependencies, operating system, and runtime (what CVE-2025-55182 enables), they cannot access your private keys.
If you need programmatic access to private key signatures, you need a TEE. Without these isolation guarantees, you’re one CVE in your dependency tree from massive disaster.
There are many TEE offerings out there, but many require complex deployment. We chose to build our solutions with AWS Nitro Enclaves. Major crypto institutions widely use Nitro Enclaves; they require no specialized hardware and run entirely on AWS cloud infrastructure.
AWS Nitro Enclaves currently secure billions in crypto assets for major institutions, and you can deploy the same technology on your own infrastructure today.
High-Level Architecture
The Nitro Enclave architecture separates your key management system into two separate processes, and a tight integration with AWS KMS:
Enclave Program (Trusted Execution Environment): A program that will run in your enclave and handle signing requests over vsock (a secure local socket connection). With a tight KMS integration, you can decrypt encrypted private keys only from inside the enclave, resulting in a cryptographic guarantee that only your TEE can access the private keys. The program then loads private keys into enclave memory and returns signed transactions without exposing keys. Due to enclave resource constraints, it's common to write this program in a systems programming language like Rust or C. Package this program as a container and use the Nitro CLI to build an enclave image file (.eif). This will give you measurements for the AWS KMS integration.
AWS KMS: In IAM, you will create a KMS policy that only allows enclave images with a specific hash (derived from your trusted code) to generate symmetric keys to encrypt and decrypt private keys.
Host Program (Public Interface and Security Gateway): A program that will run on your host EC2 instance. This could be a web server or CLI tool. It will accept external signing requests and enforce security policies (IP allowlists, API authentication, transaction validation). It will forward approved requests to the enclave over vsock and return signed data to the caller.
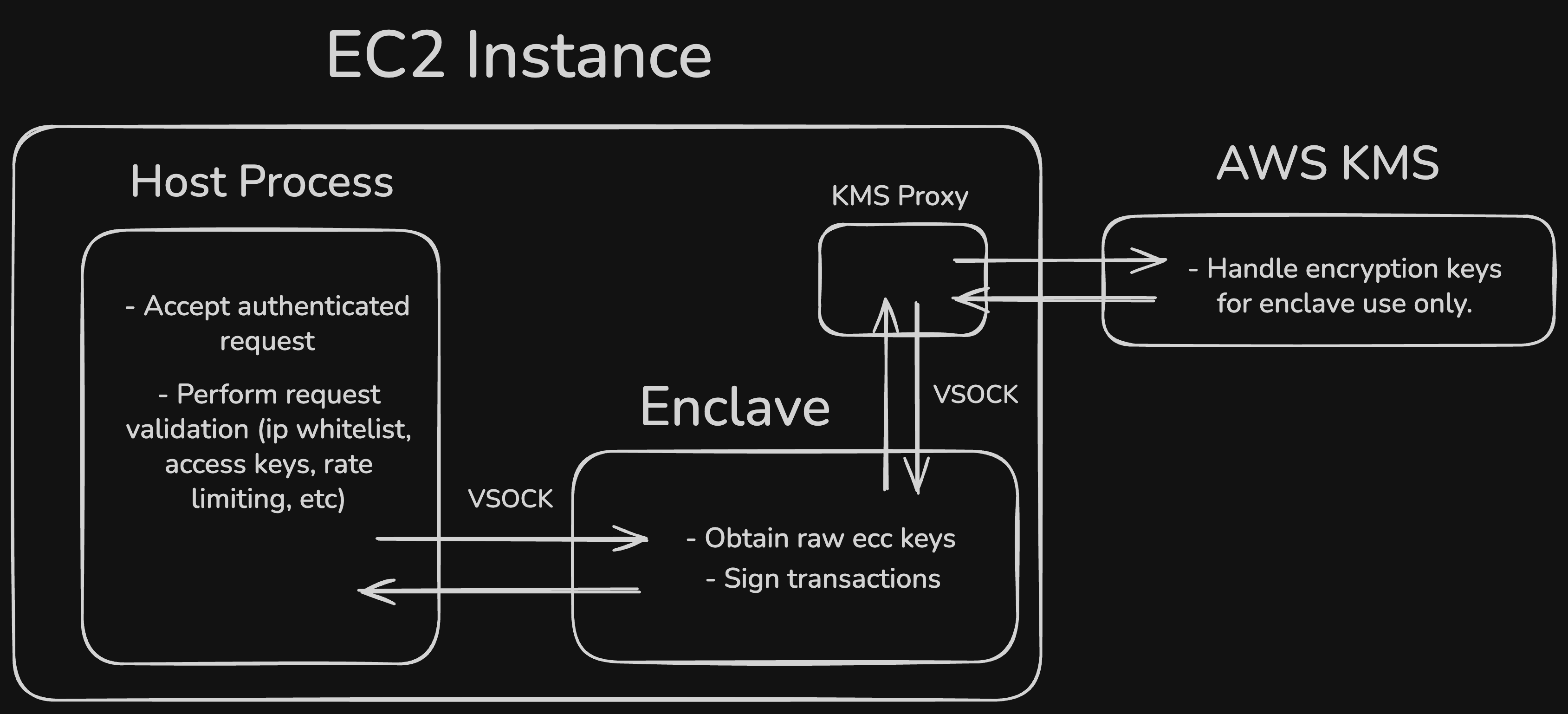
At the time of writing, the Nitro Enclave system is only supported on enclave-enabled EC2 instances. You will need to choose an appropriate EC2 instance type for your workload, configure enclave CPU and memory allocation, and handle standard EC2 administration (networking, monitoring, updates).
Partner with Experts
React CVE-2025-55182 is not the first pre-authentication remote code execution exploit (and definitely won’t be the last). We provide a self-hosted and self-custodial solution with enterprise-grade security using the same architecture outlined in this article. It’s designed for organizations like yours that need institutional-grade key security without the engineering overhead.